Diabetes Support, Strategies, and Hope
Managing Diabetes, Living Fully. Taking Control, One Blood Sugar at a Time
What is diabetes?
When we eat or drink, our body breaks that food or drink down into small units of sugar. That sugar then goes into our blood. When our body detects that rise in blood sugar, it releases a hormone called ‘insulin’ from an organ called the ‘pancreas’. Insulin’s job is to move the blood sugar into our body stores and our organs (e.g.
liver). When the body either lacks insulin (e.g. because the pancreas is not working) or the organs are unable
to respond to the insulin, we become sick and have a medical condition called ‘diabetes’.
- Type 1 diabetes = lack of insulin
- Type 2 diabetes = lack of organ response to insulin
Diabetes happens because either the pancreas is sick and is not able to produce insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or because all the organs ‘insulin detection systems’ are sick and they cannot respond to insulin (Type 2 diabetes). Either way, the net result is the same: high levels of blood sugar which damage the body.


Why is diabetes so serious?
High levels of blood sugar can damage the body in many ways, including:
- Heart and blood vessel disease
Diabetes can make it harder to control blood pressure and cholesterol, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other blood vessel problems. - Nerve damage
Also known as ‘diabetic neuropathy’, nerve damage can cause pain, burning, tingling, and loss of feeling. It can also make it harder for men to have an erection. - Kidney damage
Also known as ‘diabetic nephropathy’, kidney damage can be painless and doesn’t cause symptoms until it’s advanced. - Eye damage
Also known as ‘diabetic retinopathy’, eye damage can lead to vision loss and blindness. Regular eye exams can help prevent up to 90% of diabetes-related blindness. - Foot damage
Foot problems, like sores and infections, can lead to amputation if not treated. - Skin and mouth conditions
Diabetes can cause skin conditions, and extra glucose in the blood can increase the chance of gum disease and infections. - Immune system problems
Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making people more likely to have serious complications from common infections. - Other complications
Diabetes can also increase the risk for dementia, bone diseases, and depression.
What can we do about it?
The main treatments options currently used around the world are.
- To control the diet and other lifestyle activities (e.g. stopping smoking).
- To give insulin injections into the body (because the pancreas cannot make insulin)
- To give medicines that encourage the pancreas to make more insulin
- To give medicines that make organs more responsive to insulin.
Current standard medical treatment can only help to treat symptoms by keeping the blood sugar under control, in the hope of reducing the chances that the above complications will occur. Unfortunately, this means being dependent on treatment (injections, tablets etc.) for your whole life. Despite this, sadly, the end result of lifelong diabetes is often the same: death or disability due to one or more of the above complications of diabetes. If all else fails, sometimes patients may also need transplant surgery to replace their pancreas.
Advanced treatment consists of:
- Reducing risk factors that prevents diabetes from occurring
- Reversing the disease process of diabetes, if diabetes has already occurred.
New advanced medical treatment offered by CBE has the potential to treat the root cause of diabetes as well as eliminate the risk factors that can create diabetes in the first place, giving rise to the possibility of a long-term solution, without needing any injections or medicines. This means that the above complications can be avoided completely. To achieve this outcome, two treatment modalities are required: hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) and laser acupuncture therapy (LAT).
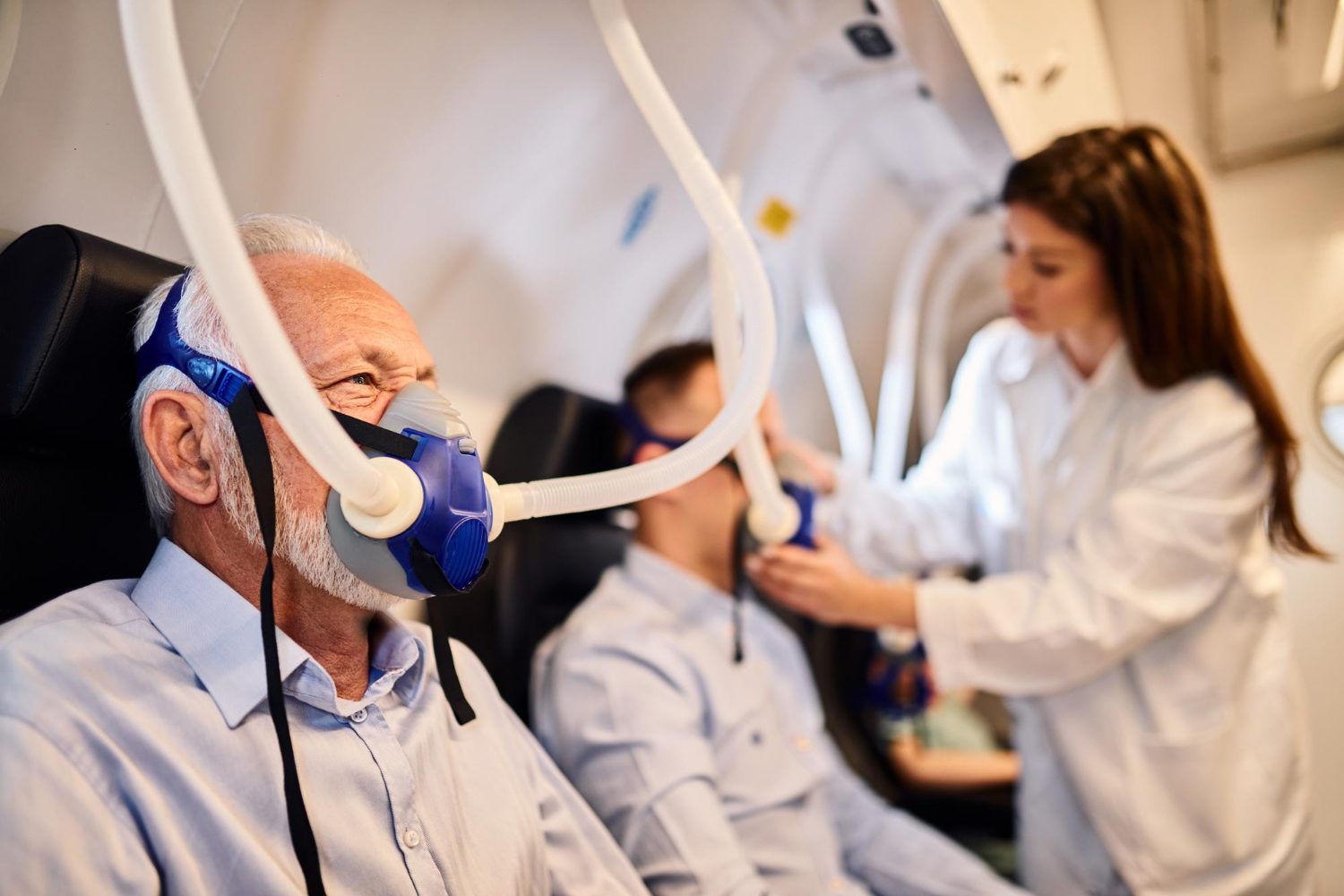
This is why we use only medical grade hard chambers in our facility:
- Our medical grade hard chambers can deliver up to 900% more oxygen (medicine) than a soft chamber. A simple oxygen mask hooked up to an oxygen tank can deliver more oxygen than a soft chamber. For a more in-depth discussion of this issue, see Explaining the Math for Hyperbaric Oxygen by Dr. Caroline Fife (published Feb 6, 2018 in Hyperbaric Medicine / Today’s Wound Clinic and associated table
- All valid scientific studies demonstrating the benefit of hyperbaric oxygen therapy were performed at pressures higher than those able to be achieved in a soft chamber. You can’t extrapolate those benefits at the much lower pressures generated from soft chambers.
- None of the government regulatory bodies in Europe and North America (FDA in the USA, the MHRA in the UK etc.) recognize soft chambers as a medical device for hyperbaric oxygen treatment, and you will not find them in any reputable hospital or medical office. The government regulatory bodies only
recognise soft chambers as a device used to treat altitude sickness during transport to a definitive medical facility. - Scientific literature shows that oxygen becomes bacteriostatic (biological or chemical agent that prevents bacteria from reproducing) at 1.5 ATA. Since soft chambers can only produce 1.3 ATA they are not able to prevent bacteria from growing; in fact, they can actually enhance the growth of some
molds, fungus, and aerobic bacteria. (Note: ATA refers to atmospheres absolute. One atmosphere
absolute or 1 ATA is the average atmospheric pressure exerted at sea level.) - These inflatables are often called “hyperbaric chambers” in contrast to “hyperbaric oxygen chambers.” Be wary of confusing the two.
For greater detail on the subject, the Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society Safety Committee has published a Special Report that addresses the safety concerns of these inflatable chambers.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can help with some symptoms of type 1 diabetes and wound healing in a
number of ways, including:
- Improving lipid profile: A pilot study found that HBOT can improve the fatty acid composition in patients with type 1 diabetes.
- Increasing insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1): HBOT can increase the expression of IGFBP-1, which can decrease serum insulin levels.
- Accelerating wound healing: HBOT can help diabetic foot ulcers heal by increasing oxygen dispersion to damaged tissues, reducing inflammation, and killing anaerobic bacteria.
- Improving glycaemic control: HBOT can reduce fasting blood glucose levels and increase insulin sensitivity.
- Stimulating angiogenesis: HBOT can stimulate the growth of new blood vessels.
- Helping with neuropathy: HBOT can help heal nerves in the extremities and bring back blood flow.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can also improve insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in people with type 2 diabetes:
- Insulin sensitivity: HBOT can increase insulin sensitivity in the tissues of people with type 2 diabetes. This effect can be seen within 30 minutes of exiting the hyperbaric chamber.
- Glucose tolerance: HBOT can improve glucose tolerance in people with type 2 diabetes. This includes reducing fasting blood glucose and decreasing glycemia after an oral glucose tolerance test.
- Pancreatic β-cell function: HBOT can reduce the rate of apoptosis (cell death) in pancreatic β-cells.
- Hepatic glycogen storage: HBOT can increase hepatic glycogen storage in people with type 2 diabetes.
There is growing evidence that HBOT can completely cure type 2 diabetes in a select subset of patients.
Regarding risk factors for diabetes, HBOT (and sometimes combined with laser acupuncture) can tackle the following conditions that are known to increase the chances of developing diabetes:
- Obesity: Studies have found that being overweight in early life increases the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. For example, one study found that for each standard deviation increase in BMI, the risk of developing type 1 diabetes increased by about 25%. Another study found that weight gain in the first
year of life was positively associated with the development of type 1 diabetes. Increased BMI in the first trimester of pregnancy can also increase the risk of type 1 diabetes in the child. While weight doesn’t cause type 1 diabetes, losing weight can help reduce the risk of complications and the amount of
insulin needed. Being overweight or obese, especially with central obesity also accounts for 80–85% of the overall risk for developing type 2 diabetes.We are also able to improve weight management using laser acupuncture. How much weight loss is achieved depends on the starting weight and level of motivation. Those who are only mildly overweight can lose typically 5-6kg in one month. Those who are severely overweight can lose up to 30-40kg in one month.
Laser acupuncture can help with weight loss by stimulating acupuncture points with lasers to:
- Increase metabolism: Laser acupuncture can accelerate metabolism.
- Reduce appetite: Laser acupuncture can reduce hunger by stimulating the hypothalamus, which controls appetite. Acupuncture can also produce serotonin, which reduces appetite.
- Improve blood circulation: Laser acupuncture can improve blood circulation, which can reduce tissue damage and inflammation.
- Reduce stress: Acupuncture can reduce stress and despair, which can help reduce hunger.
Laser acupuncture is intended to be used in combination with eating healthy and exercising lightly. It’s not a “magic wand” for weight loss, but it can help people reach their ideal weight in a natural, permanent way. We, at the Centre for Bioenergetics, may therefore recommend complementing laser acupuncture treatment for weight loss with dietitian support on a case-to-case basis.
- Smoking: Smoking increases blood sugar levels and leads to insulin resistance. In fact, smokers are 30– 40% more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than non-smokers, and the more you smoke, the higher your risk. We at CBE use laser acupuncture to help patients give up smoking. 96% of our patients do so after only two treatment sessions.
Laser acupuncture for smoking cessation works by stimulating the release of endorphins, which can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms:
- How it works
A laser is applied to specific acupuncture points on the body, such as the hands, ears, nose, and wrists. This stimulates the release of endorphins, such as serotonin and dopamine, which can help reduce feelings of anxiety and craving. - How it compares to other methods
Laser acupuncture is more effective than other methods for quitting smoking, such as patches, gum, or e-cigarettes. - How long it lasts
After the initial treatment (2 sessions). In most cases (96%), this is all that is needed for a permanent effect. However, in a few people, a booster session is needed after 6-9 months for a more longterm/permanent effect.In short, with scientific knowledge of the specific wavelength, frequency, dosage etc. we can use acupuncture locations on the human body to channel bioenergetic fluxes in a positive way, so that a person no longer feels the addiction or desire to smoke.
- Cholesterol: Having high cholesterol or low levels of LDL, or “good” cholesterol, can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, as can having high triglyceride levels. HBOT has been shown to reduce both cholesterol and triglyceride levels, thereby reducing not only the risk of diabetes but also heart attacks
and strokes. - Medications: Statins, corticosteroids, and combined treatment with a thiazide diuretic plus a betablocker, can increase the risk for developing hyperglycaemia and type 2 diabetes. HBOT can alleviate the need for such medications, by treating the root medical conditions.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): This increases the risk of non-diabetic hyperglycaemia and type 2 diabetes. HBOT has been shown scientifically to effectively treat PCOS.
- Metabolic syndrome: Insulin resistance is commonly associated with the metabolic syndrome, defined as a combination of raised blood pressure, dyslipidaemia, fatty liver disease, central obesity, and a tendency to develop thrombosis. HBOT can treat these root causes and reverse metabolic syndrome.
- Diet: A low-fibre, high glycaemic index (GI) diet may increase the risk of being overweight or obese. High-GI foods contain carbohydrates that are broken down quickly and cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels, such as sugary foods and drinks, white rice, white bread, and potatoes. We at CBE work with specialist dietitians to help patients overcome their dietary risk factors.
- Physical activity: Being physically active less than three times a week increases risk of type 2 diabetes. Patients benefit from the specialist advice and guidance from our physiotherapists.
- Blood pressure: Having high blood pressure increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. Laser acupuncture treatment has been scientifically shown to be effective in reducing blood pressure.
All other risk factors are ‘non-modifiable’ (i.e. there is nothing that can be done about them):
- Genetics, Family history & Ethnicity: A sibling of a person with type 1 diabetes has 6–7% risk of developing it themselves. This risk increases to 30–70% in identical twins. The risk for a child is 1–9% if a parent has type 1 diabetes. Having a close relative with type 2 diabetes, such as a parent or sibling. People with a family history of diabetes are 2–6 times more likely to have diabetes than people without a family history. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is about 15% if one parent has type 2 diabetes, and 75% if both parents have type 2 diabetes. People of Asian, African, and Afro-Caribbean ethnicity are 2–4 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than white people.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children, teens, or young adults, but it can occur at any age. Being 45 or older increases risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Environmental factors: These can trigger the development of autoimmunity (i.e. ‘when the body attacks itself’) to the pancreatic beta cells. Some environmental factors include:
- Diet
- Vitamin D exposure
- Obesity
- Early-life exposure to viruses associated with islet inflammation
- Decreased gut-microbiome diversity
- Gestational diabetes: Having ever had gestational diabetes or given birth to a baby who weighed over 9 pounds (approx. 4kg) increases risk. Women with a history of gestational diabetes have a seven-fold increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Children born to mothers with gestational diabetes have a six-fold increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes.
- Low birth weight for gestational age: There is some evidence that preterm birth before 35 weeks of gestation is associated with an increased risk for type 2 diabetes developing in adult life.
We cannot change what we are born with (e.g. genetics, birth weight etc.) but we can lower our risk of diabetes by changing our lifestyle and, through the use of HBOT and laser acupuncture as well as with the help of healthcare professionals such as dietitians and physiotherapists, keep all the other risk factors at bay. The overall impact of this is that patients can keep away from diabetes altogether or, at the very least, delay it for a very long time.
Are you ready to get your diabetes treated by the Centre for Bioenergetics? Get In Touch.
