Photodynamic Therapy
Light Up Healing: The Power of Photodynamic Therapy. Brighter Solutions for Healthier Tomorrows. Target. Activate. Heal.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) can disrupt mitochondrial bioenergetics. PDT is a treatment that uses a photosensitizer drug and light to destroy diseased tissue and abnormal cells (e.g. cancer cells). The photosensitizer is activated by light, which triggers a series of reactions that create reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS damage cells, which can lead to cell death.
Here are some ways that PDT can impact mitochondrial bioenergetics:
- Photosensitizer azure A (AA)
AA can diminish the amount of cellular ATP and increase oxygen uptake. It can also inhibit gluconeogenesis and ureogenesis, while stimulating glycogenolysis and glycolysis. - Mitochondrial metabolism
Drugs that target different parts of mitochondrial metabolism have been proposed as potential cancer therapies. For example, metformin can block complex I of the ETC in mitochondria, which can lower oxygen consumption.
PDT has several advantages over other therapeutic modalities, including its selectivity against tumour cells.
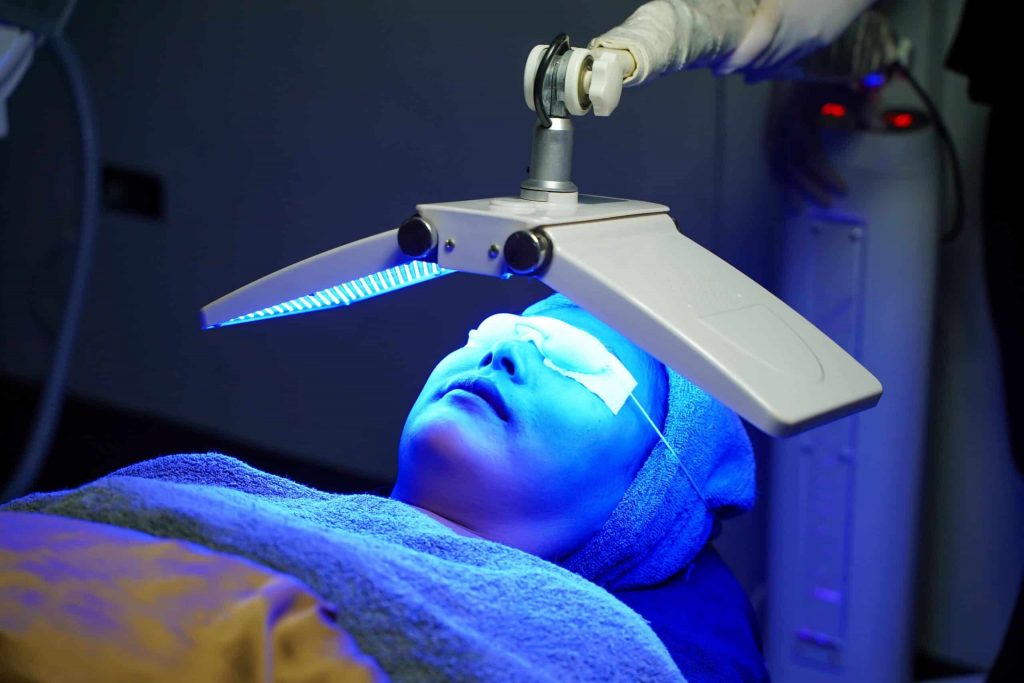
PDT can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including:
- Cancer: PDT can treat certain types of cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma (BCC). The drug is administered as a cream, liquid, or injection, depending on the type of cancer. The light is then shone on the treatment area, either directly or through a scope.
- Skin conditions: PDT can treat sun damage, actinic keratoses, acne, and psoriasis.
- Eye conditions: PDT can treat wet age-related macular degeneration. An eye doctor injects the drug into a vein in the arm, and then shines a laser into the eye.
- Other conditions: PDT can also treat herpes.
PDT is usually performed as an outpatient procedure. The treatment involves the following steps:
- Apply the light-sensitive drug to the treatment area
- Wait a period of time, which can be several hours or days, depending on the type of cancer
- Shine a light on the treatment area
The light activates the drug, causing a reaction that damages nearby cells. The treatment can cause a stinging or burning sensation, but painkillers, a fan, or a numbing injection can help.
PDT has some advantages over other treatments, including being less invasive than surgery, costing less, and
having no long-term side effects when used properly. However, it has some limits, such as not being able to
treat large cancers or cancers that have spread.

