Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
The Power of Oxygen for a Healthier You. Revitalize Your Body, One Breath at a Time
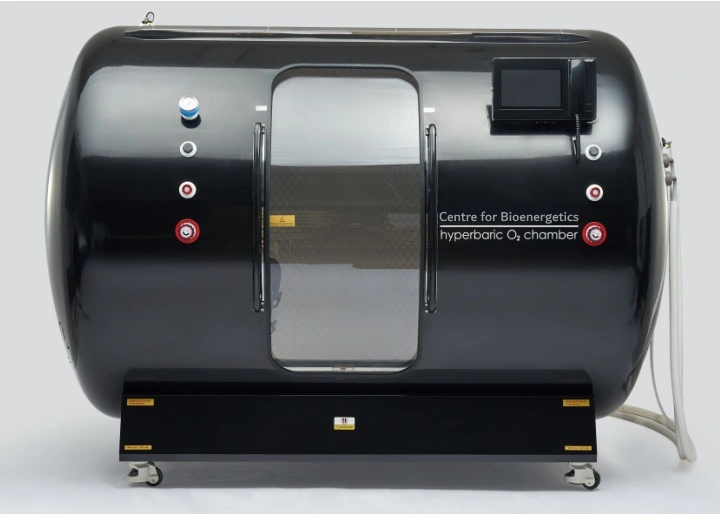
HBOT involves breathing 100% oxygen in a hyperbaric chamber at a pressure of 2 to 3 atmospheres absolute (ATA). There are two types of hyperbaric oxygen chambers: monoplace chambers for one person and multiplace chambers for two or more people.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can affect intracellular bioenergetics in a number of ways, including:
- Mitochondrial biogenesis: HBOT can cause changes to mitochondrial motility and respiratory function.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can promote mitochondrial biogenesis:
1. Mitochondrial redox: HBOT can improve mitochondrial redox, which is important for cellular function.
2. Mitochondrial integrity: HBOT can preserve mitochondrial integrity.
3. Transcription factors: HBOT can activate transcription factors.
4. Oxidative stress: HBOT can alleviate oxidative stress.
5. Neuroprotection: HBOT can promote neuroprotection.
6. SIRT-1/PGC-1α pathway: HBOT can stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis through the SIRT-1/PGC1α pathway.
- Mitochondrial dynamics: HBOT can cause changes to mitochondrial motility and respiratory function.
- Intracellular bioenergetic capacity: HBOT can alter the intracellular distribution of cellular bioenergetic capacity.
- Cell migration and proliferation: HBOT can cause undesirable and persistent alterations in bioenergy function that are needed for cell migration and proliferation.
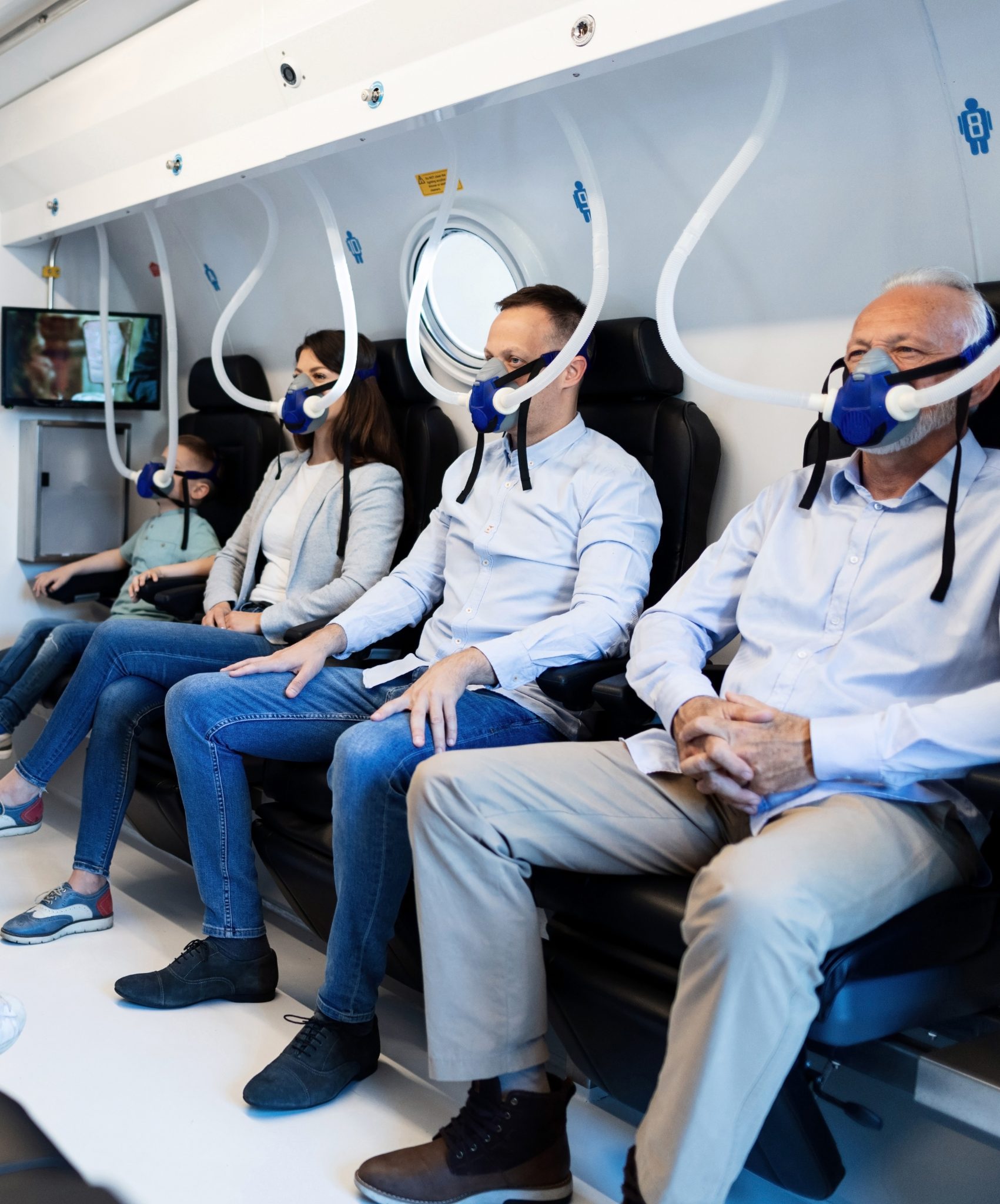


HBOT has the following clinical benefits:
- Increases oxygen in the lungs
The higher air pressure in the chamber allows the lungs to collect more oxygen than normal. - Delivers oxygen to tissues
The extra oxygen is delivered to tissues that need it to heal and fight infection - Reduces swelling
HBOT can reduce swelling caused by damaged blood vessels leaking fluid into tissues. - Prevents reperfusion injury
HBOT can prevent the severe tissue damage that occurs when blood flow returns to oxygen-deprived tissues - Strengthens the immune system
HBOT can help block harmful bacteria and increase the concentration of oxygen in tissues, which helps them resist infection. - SIRT-1/PGC-1α pathway:
HBOT can stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis through the SIRT-1/PGC1α pathway. - Promotes healing
HBOT can encourage the formation of new collagen and skin cells by stimulating the growth of new blood vessels.
There are two types of HBOT chambers: soft shell and hard shell (sometimes called ‘medical grade’).
Medical grade hard-shell hyperbaric chambers are more effective and efficient than soft-shell chambers for a number of reasons, including:
- Pressure
Hard-shell chambers can deliver up to nine times more oxygen than soft chambers and can reach higher pressures. Hard-shell chambers are also more rigid and can control pressure more precisely than soft chambers - Oxygen purity
Hard-shell chambers can deliver 100% oxygen, while soft chambers typically only deliver around 24% - Durability
Hard-shell chambers are more durable, have a longer lifespan, and are easier to clean and maintain - Clinical use
Hard-shell chambers are commonly used in clinical settings and specialized hyperbaric oxygen therapy centres. - Scientific studies
All scientific studies that have shown the medical benefits of hyperbaric oxygen therapy were performed using hard-shell chambers.
This is why we use only medical grade hard chambers in our facility:
- Our medical grade hard chambers can deliver up to 900% more oxygen (medicine) than a soft chamber. A simple oxygen mask hooked up to an oxygen tank can deliver more oxygen than a soft chamber. For a more in-depth discussion of this issue, see Explaining the Math for Hyperbaric Oxygen by Dr. Caroline Fife (published Feb 6, 2018 in Hyperbaric Medicine / Today’s Wound Clinic and associated table
- All valid scientific studies demonstrating the benefit of hyperbaric oxygen therapy were performed at pressures higher than those able to be achieved in a soft chamber. You can’t extrapolate those benefits at the much lower pressures generated from soft chambers.
- None of the government regulatory bodies in Europe and North America (FDA in the USA, the MHRA in the UK etc.) recognize soft chambers as a medical device for hyperbaric oxygen treatment, and you will not find them in any reputable hospital or medical office. The government regulatory bodies only
recognise soft chambers as a device used to treat altitude sickness during transport to a definitive medical facility. - Scientific literature shows that oxygen becomes bacteriostatic (biological or chemical agent that prevents bacteria from reproducing) at 1.5 ATA. Since soft chambers can only produce 1.3 ATA they are not able to prevent bacteria from growing; in fact, they can actually enhance the growth of some
molds, fungus, and aerobic bacteria. (Note: ATA refers to atmospheres absolute. One atmosphere
absolute or 1 ATA is the average atmospheric pressure exerted at sea level.) - These inflatables are often called “hyperbaric chambers” in contrast to “hyperbaric oxygen chambers.” Be wary of confusing the two.
For greater detail on the subject, the Undersea & Hyperbaric Medical Society Safety Committee has published a Special Report that addresses the safety concerns of these inflatable chambers.
